Steel structure buildings are known for their strength, durability, and versatility. But what truly holds them together? The answer lies in steel connections. Though often hidden, connections are vital for ensuring stability, safety, and performance. From skyscrapers to industrial facilities, the right connection makes all the difference.
In this guide, we’ll explore the types of steel connections, their practical applications, and key design considerations for long-lasting results.
Types of Steel Connections
Steel connections are the joints that link structural members together. There are five main types, each with unique features, benefits, and applications.
Bolted Connections
Bolted connections use bolts and nuts to fasten members. They are versatile, cost-effective, and easy to install. High-strength bolted joints are widely used in seismic zones for reliability.
- By Force Combination: Axial + Shear, Moment + Shear
- By Force Type: Axial, Shear, Moment connections
- By Load Transfer: Bearing-type, Friction-type (slip-critical)
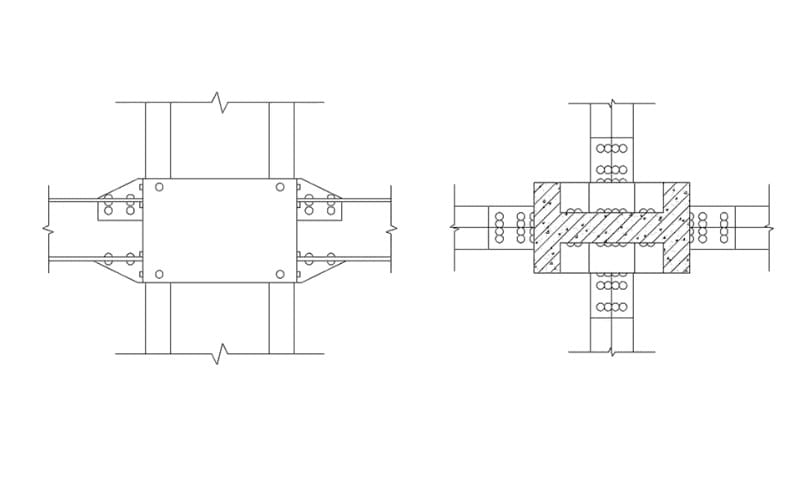
Welded Connections
Welded connections fuse components using heat to create a permanent joint. They offer exceptional strength and seamless appearance, but require skilled labor and precision.
- By Weld Type: Fillet welds, Groove welds
- By Load Transfer: Shear-resisting, Moment-resisting
- By Fabrication: Shop welds, Field welds
Riveted Connections
Riveted joints, once standard in steel construction, are less common today but remain in use for heritage restoration and classic structures.
Hybrid Connections
Hybrid connections combine bolting and welding, offering both strength and flexibility—ideal for complex structures.
Pinned and Fixed Connections
- Pinned connections: Allow rotation, common in trusses and arches.
- Fixed connections: Restrict rotation, ensuring high stability in rigid frames.
Comparison of Steel Connection Types
| Connection Type | Key Features | Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bolted | Fastened with bolts & nuts; bearing or friction types | Easy installation, adjustable, cost-effective | Beam-to-column joints, seismic zones |
| Welded | Permanent joints fused with heat | Strong, rigid, seamless | High-rise buildings, bridges, architectural projects |
| Riveted | Mechanical joint using hot rivets | Historic durability, vibration resistance | Heritage restoration, old bridges |
| Hybrid | Combination of bolting + welding | Strength + flexibility | Complex or large-span structures |
| Pinned | Allow rotation, no moment resistance | Flexible, reduces stress | Trusses, arches, roof structures |
| Fixed | Restrict rotation, rigid load transfer | High stability, resists bending | Rigid frames, skyscrapers |
Practical Roles in Structural Systems
Steel connections do more than hold elements together—they ensure load distribution, flexibility, and safety.
- Load Distribution: Transfers vertical and lateral forces safely.
- Flexible Layouts: Enables open spaces in warehouses and malls.
- High-Rise Stability: Column base connections anchor tall buildings against wind and seismic forces.
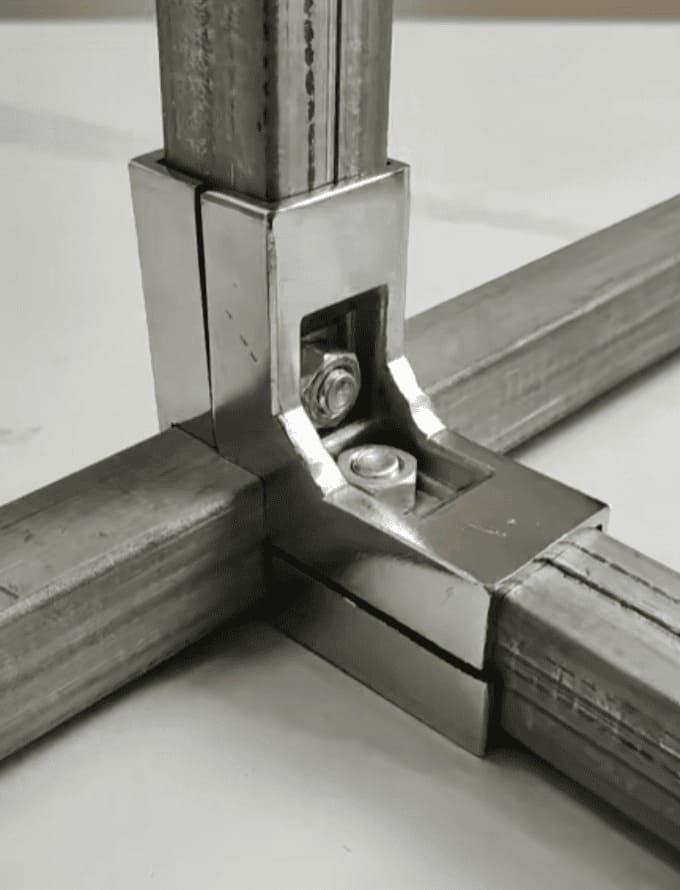

Design Considerations
When designing connections, engineers focus on:
- Load Transfer – handling axial, shear, and moment forces.
- Material Compatibility – preventing corrosion and expansion issues.
- Fabrication & Installation – precision is critical for safety.
- Durability & Maintenance – ease of inspection and repair extends service life.
Challenges and Common Issues
- Fatigue & Stress Concentration: Prevent with proper design and reinforcements.
- Corrosion: Use protective coatings and resistant alloys.
- Misalignment: Ensure precision in fabrication and installation.
Innovations in Steel Connections
- Advanced Materials: High-strength steels, corrosion-resistant alloys.
- Smart Connections: Sensors for real-time monitoring and maintenance.
- Prefabricated Joints: Faster, more precise, and cost-efficient construction.
Finding a Trusted Steel Structure Manufacturer
Steel connections are the foundation of safe, durable buildings. From bolted and welded joints to hybrid and fixed connections, each plays a vital role in modern construction.
At Best Steel Structure, we specialize in seismic-resistant bolted connections and precision-welded joints. Our tailored solutions guarantee strength, efficiency, and long-term durability.
👉 Contact us today to build structures that combine safety, innovation, and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are steel connections in building structures?
Steel connections are joints that link beams, columns, and other structural elements, allowing loads to transfer safely and maintaining the stability and integrity of the structure.
2. What are the main types of steel connections?
The main types include bolted, welded, riveted, hybrid, pinned, and fixed connections. Each type has unique features, advantages, and typical applications.
3. How do bolted and welded connections differ?
- Bolted connections: Use bolts and nuts, easy to install and adjust, suitable for seismic zones.
- Welded connections: Use heat to fuse steel members, creating strong and rigid joints, ideal for high-rise buildings and bridges.
4. What factors affect the design of steel connections?
Key considerations include load transfer (axial, shear, moment), material compatibility, fabrication precision, installation quality, and maintenance accessibility.
5. How can steel connection durability be ensured?
Durability can be enhanced by using corrosion-resistant materials, protective coatings, regular inspections, and proper maintenance.
6. What are the advantages of hybrid steel connections?
Hybrid connections combine bolting and welding, offering both flexibility and strength. They are ideal for complex or large-span structures.
7. Can steel connections be used in prefabricated or modular construction?
Yes. Prefabricated steel connections allow for off-site fabrication, faster assembly, high precision, and reduced on-site labor, making them perfect for modular buildings and industrial facilities.
8. How do modern innovations improve steel connections?
Innovations such as smart sensor-equipped connections, high-strength alloys, and prefabricated joints enhance monitoring, strength, precision, and reduce long-term maintenance costs.



