A steel beam splice connection joins two beams into one continuous unit. It is essential when beam length exceeds manufacturing or transport limits, or when complex designs require longer spans.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
What a beam splice is and why it matters.
Where to place (and avoid) splices.
The main splice connection methods.
A step-by-step splicing process.
Factory-direct splice plate and bolt solutions.
📌 What Is a Steel Beam Splice?
A steel beam splice connects two beams into a single structural member, transferring loads safely across the joint.
A typical splice includes:
Splice plates – attached to beam webs or flanges.
Fasteners – bolts or welds securing the plates.
Reinforcements – stiffeners or supports for added stability.
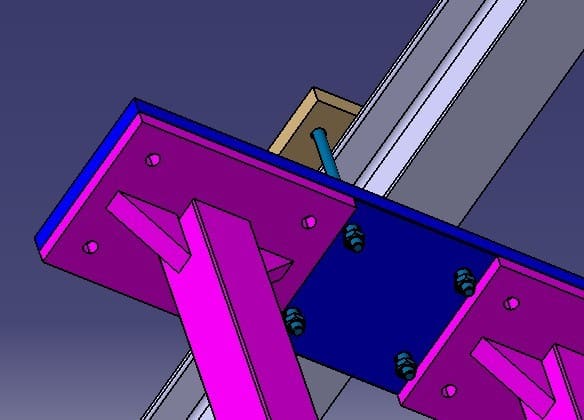
Splicing is necessary because:
Long spans cannot always be manufactured in one piece.
Transport restrictions limit beam size.
Complex or curved designs require sectional assembly.
⚙️ Why Beam Splicing Matters
Safety: Proper splicing distributes bending and shear forces, improving resistance to earthquakes, fatigue, and wind.
Cost Efficiency: Shorter beams lower production and transport costs. Standard splice kits reduce labor.
Sustainability: Enables reuse of leftover beam sections, reduces waste, and supports the circular economy.
Design Flexibility: Makes long spans, curved beams, and special structures possible.
📍 Where to Place or Avoid a Steel Beam Splice
Recommended Placement
Near supports (first third of the span).
Low-stress zones away from maximum bending moments.
Code-compliant positions per IS, AISC, GB standards.
Avoid Placement
High-stress areas (mid-span, cantilever ends).
Dynamic load zones (bridges in seismic areas, vibrating floors).
Fireproofing or corrosion-critical areas.

🏗️ When Is Splicing Needed?
Structural limits: Long-span stadiums, airports, bridges.
Transport limits: Beams delivered in shorter sections.
Cost-driven: Mass production of shorter beams reduces costs.
Design needs: Curved, tapered, or irregular beams.
🔎 Four Main Types of Beam Splice Connections
| Splicing Method | Best Use | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bolted Splice | Temporary frames, sites with poor welding | Quick install, removable, good for remote projects | Lower fatigue resistance, precise hole drilling needed |
| Welded Splice | Bridges, high-rises, permanent structures | Seamless strength, clean appearance | Slower, skilled welders required, weather-sensitive |
| Hybrid (Bolt + Weld) | Heavy-duty plants, mixed loads | Combines bolt flexibility + weld strength | Complex process, higher cost |
| Innovative (e.g. Mechanical Locking) | Offshore platforms, modular projects | Fast, precise, no welding | Expensive, limited adoption |

6-Step Standard Splicing Process
Design Phase
Calculate loads (bending, shear, axial).
Select splice method.
Prepare drawings with plate sizes, bolt layout, and weld specs.
Material Preparation
Mill or bevel beam ends.
Fabricate splice plates and drill holes.
Prepare bolt kits.
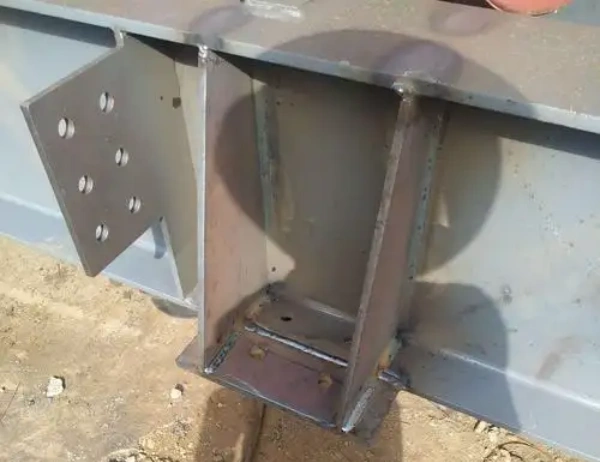

On-Site Alignment
Use temporary supports.
Align with lasers.
Inspect plates, holes, weld surfaces.
Connection Construction
Bolted: Tighten in sequence.
Welded: Controlled weld, stress relief.
Hybrid: Pre-tighten bolts, then weld.
Quality Inspection
Ultrasonic weld testing.
Torque verification.
Alignment monitoring.
Protection Measures
Grind seams for coating.
Apply corrosion and fireproof coatings.
❓ FAQs on Steel Beam Splicing
Q1: Best location for a steel beam splice?
👉 In low-stress zones, near supports or low shear areas. Avoid mid-span and cantilever ends.
Q2: Difference between bolted and welded splice joints?
👉 Bolted = quick, removable, for temporary projects. Welded = permanent, stronger, used in high-rises/bridges.
Q3: Can splice plates be customized?
👉 Yes, Best Steel Structure manufactures custom plates with various thicknesses, materials, and hole patterns.
Q4: Which standards apply to splice design?
👉 IS 800, AISC 360, GB 50017. Best Steel Structure ensures compliance with all major codes.
Q5: Does Best Steel Structure supply factory-direct splice kits?
👉 Yes, with certified splice plates, bolts, and welded solutions at wholesale cost.
🏭 Factory-Direct Supply of Splice Solutions
Best Steel Structure offers:
Certified splice plates, bolts, and welded kits.
Compliance with IS, AISC, GB, Eurocode standards.
ISO & CE-certified production with up to 50-year warranty.
Annual capacity: 120,000 tons, supporting 1,000+ projects globally.
Complete service: design, fabrication, installation, after-sales support.
Contact us today at rena@besteelstructure.com or via WhatsApp for free consultation and wholesale pricing.



