Do Steel Garages Need Footings? Here’s What You Should Know
When building a steel garage, one of the most common questions is: Do I really need footings?
The short answer: Yes — most steel garages require footings to ensure the structure’s stability, durability, and safety. Footings act as the strong base that supports your entire building, preventing shifting or settling over time.
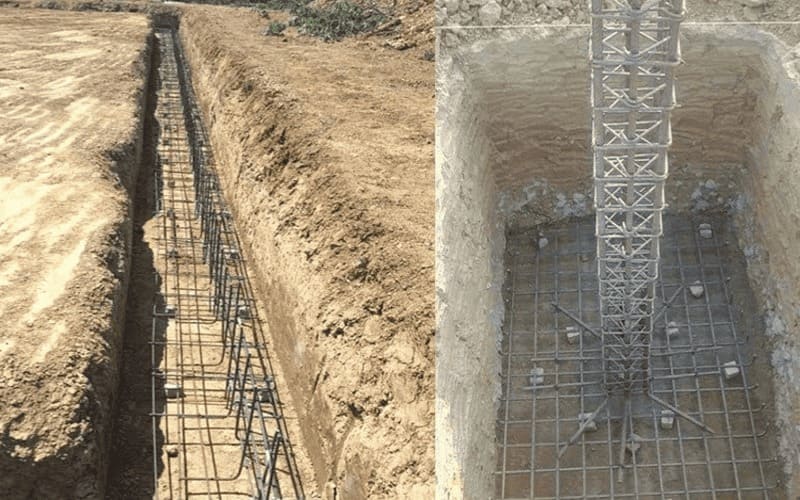

But how do you know what type of footing your project needs?
This guide explains everything — from footing basics to how soil, climate, and garage size affect your foundation design. You’ll also learn about the main types of footings and how to plan for them properly.
What Are Footings and Why Are They Important?
Footings are the foundation base beneath your steel garage — the “feet” that distribute the building’s weight evenly across the ground.
Typically made of reinforced concrete, they keep your structure stable and prevent it from sinking or shifting. Think of them as the roots anchoring your steel garage securely to the earth.
| Footing vs Foundation | Function |
|---|---|
| Footing | Supports the structure by spreading the load into the soil |
| Foundation | Transfers the overall building weight to the footings |
Do I Really Need Footings for My Steel Garage?
Yes — in most cases, you do. Here’s why footings matter:
Larger or heavier garages: If your garage will store vehicles or heavy tools, footings distribute the load evenly, reducing ground settlement.
Poor soil conditions: Soft or moist soil lacks stability; footings provide a solid base and prevent sinking.
Building codes: Many local regulations require permanent footings for large or enclosed steel structures, especially in frost-prone or seismic regions.
⚠️ Common Mistake:
Some believe smaller garages don’t need footings — but skipping them can cause structural damage, uneven doors, or even collapse over time.

How Soil and Climate Affect Footing Design
Soil type and environmental conditions are crucial factors when designing your steel garage footings.
1. Unstable Soil Conditions
Soft, loose, or wet soil has a low bearing capacity. To prevent settling or tilting:
Increase footing depth to reach solid layers (usually 18–24 inches).
Widen the base area to distribute load evenly (strip or slab footings are ideal).
Stabilize soil through compaction or reinforced layers.
2. Cold Climates and Frost Heave
In colder areas, soil freezes and expands, pushing footings upward — known as frost heave.
To prevent damage:
Build below the frost line (typically 36 inches or more).
Use reinforced or insulated footings.
Install drainage systems to keep soil dry and stable.

Types of Footings for Steel Garages
Depending on your garage’s size and ground conditions, here are the most common options:
| Footing Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Strip Footing | Continuous concrete under load-bearing walls | Standard garages |
| Isolated Footing | Supports individual columns | Large garages with multiple beams |
| Slab-on-Grade | Concrete slab that acts as both floor and base | Stable, level sites |
| Deep Footing | Extends deep into the ground for stability | Soft or unstable soil |
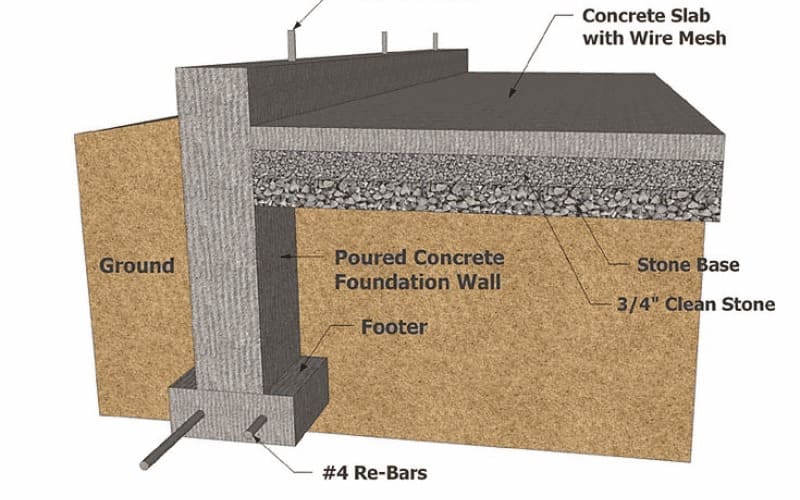
Steel Garage Footing Requirements
To ensure a durable and safe build, make sure your footings meet these standards:
Depth: At least 12 inches deep (24 inches for heavy or cold-climate garages).
Reinforcement: Use steel rebar or mesh to prevent cracking.
Concrete strength: Minimum 2,500 psi (or 4,000 psi for heavier structures).
Freeze protection: Footings must extend below the frost line in cold areas.
Drainage: Ensure ground slopes away from the garage to prevent water pooling.
How to Plan Footings for Your Steel Garage
Consult a Professional
A structural engineer can evaluate your soil and design code-compliant footings.Assess Soil Conditions
Get a soil test to determine the right footing type.Determine Garage Load
Heavier garages need deeper, reinforced footings.Check Local Codes
Ensure compliance with building regulations and frost depth standards.Budget & Timeline
Account for excavation, concrete, and curing time in your project plan.
FAQs About Steel Garage Footings
1. Can a concrete slab replace footings?
No. A slab provides a floor but lacks the strength to support structural loads. Separate footings are still required.
2. How deep should footings be?
At least 12 inches for small garages; 18–24 inches for larger ones or those in cold climates.
3. What happens if I skip footings?
You risk uneven settling, cracking, or even structural failure.
4. Should I test my soil first?
Yes. A professional soil test ensures proper footing design and long-term stability.
5. How long does footing installation take?
Usually 3–7 days, including excavation, concrete pouring, and curing.
6. Can prefab steel garages use standard footings?
Yes. Most prefab designs specify standard concrete footings based on size and soil type.
Final Thoughts
Proper steel garage footings are essential for safety, stability, and longevity.
By understanding your soil type, climate, and building requirements, you can design a foundation that protects your investment for decades.



